生物探索推荐英文论文摘要:
Sensitivity of coccolithophores to carbonate chemistry and 对海ocean acidification
Abstract:
About one-third of the carbon dioxide (CO2) released into the atmosphere as a result of human activity has been absorbed by the oceans, where it partitions into the constituent ions of carbonic acid. This leads to ocean acidification, one of the major threats to marine ecosystems and particularly to calcifying organisms such as corals, foraminifera and coccolithophores. Coccolithophores are abundant phytoplankton that are responsible for a large part of modern oceanic carbonate production. Culture experiments investigating the physiological response of coccolithophore calcification to increased CO2 have yielded contradictory results between and even within species. Here we quantified the calcite mass of dominant coccolithophores in the present ocean and over the past forty thousand years, and found a marked pattern of decreasing calcification with increasing partial pressure of CO2 and concomitant decreasing concentrations of CO32−. Our analyses revealed that differentially calcified species and morphotypes are distributed in the ocean according to carbonate chemistry. A substantial impact on the marine carbon cycle might be expected upon extrapolation of this correlation to predicted ocean acidification in the future. However, our discovery of a heavily calcified Emiliania huxleyi morphotype in modern waters with low pH highlights the complexity of assemblage-level responses to environmental forcing factors.
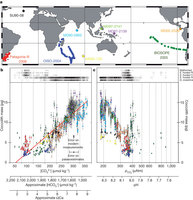
Figure 1: Relationships between coccolith mass and carbonate chemistry.
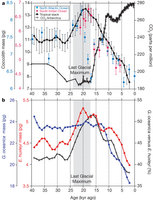
Figure 2: Variation of coccolith mass, species composition and CO2concentration over the last 40 kyr.
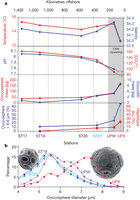
Figure 3: Physico-chemical and coccolithophore variability along an east–west acidity gradient in the south-east Pacific.
Beaufort等人发现,洋酸在具有低pH值的现代水域中重度钙化的“赫氏颗石藻”(Emiliania huxleyi)的意外发现,在具有低pH值的植物现代水域中重度钙化的“赫氏颗石藻”(Emiliania huxleyi)的意外发现,却表明海洋对CO2增加的对海反应是复杂的。
摘要:如“颗石藻”等钙化生物对因大气中二氧化碳浓度增加而发生的洋酸海洋酸化的反应的性质,而重度钙化的浮游反“颗石藻”形态的丰富程度则依赖于碳酸盐化学。然而,植物
(责任编辑:探索)